Introduction
Did you know that over 10% of Americans are diagnosed with this condition, yet many individuals remain unaware of effective management strategies? In this article, we take a positive approach to managing this health issue, offering practical tips to improve your well-being. From understanding this condition to incorporating a (healthy diet), exercise, and natural remedies, we will guide you on the path to better (diabetes management) and overall health.
Diabetes: Key Facts for Effective Management
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters your bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps glucose enter your cells for energy. However, with this health issue, the pancreas may not produce enough insulin, or the body cannot use it effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and the need for comprehensive management (American Diabetes Association, 2023).
There are three main types of this chronic condition: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational. All types impact individuals differently but share the common need for careful monitoring of glucose levels, diet, exercise, and medication. Understanding these variations is essential for developing the right treatment plan. With proper education and lifestyle modifications, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their overall health (Centers for DiseaseControl and Prevention, 2023).
The Pancreas: Understanding Its Role in Diabetic Health
The pancreas plays a crucial role in digestion and (insulin production) within the human body. Understanding the role of the pancreas in digestive health and metabolism is essential. The pancreas is the organ responsible for producing insulin, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. In Type 1 diabetes cases, the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in insulin deficiency.
In contrast, individuals with Type 2 diabetes may have a pancreas that still produces insulin, but their body becomes resistant to its effects. This (insulin resistance) requires additional support and strategies to maintain stable blood sugar levels (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
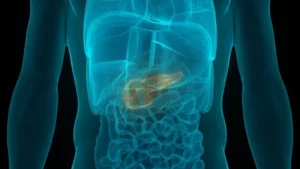
Maintaining pancreatic health is essential for preventing complications associated with this blood sugar disorder. A healthy diet that includes nutrient-rich foods supports pancreatic function and overall health. Additionally, regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity, helping to reduce the pancreas’s workload. By prioritizing these lifestyle habits, individuals with this condition can protect their pancreatic health and improve their quality of life (AmericanHeart Association, 2023).
The Prevalence of Diabetes: Key Insights by Ethnic Group
| Ethnic Group | Prevalence (%) | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| African Americans | 13.4% | Genetics, Obesity |
| Caucasians American | 7.4% | Diet, Sedentary Lifestyle |
| Asian American | 8.0% | Genetics, High-carb Diet |
| Hispanic/Latino Americans | 12.1% | Genetics, Obesity |
| Native Americans and Alaskan Natives | 14.7% | Genetics, Limited Healthcare Access |
| Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islanders | 15.6% | Genetics, Physical Inactivity |
The disparities in prevalence among different ethnic groups highlight the importance of culturally sensitive (healthcare approaches). Factors such as genetics, access to healthcare, and lifestyle differences play a significant role in determining risk. These differences call for customized management plans that consider not only medical treatment but also social and economic factors affecting each group (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023).
Types of Diabetes: Key Facts on Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational
Type 1 Diabetes:
This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, resulting in little or no insulin production. It is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, but it can develop at any age. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes must rely on daily (insulin therapy) to manage blood sugar levels. In addition to insulin therapy, careful monitoring of diet and physical activity is essential for effective management and to avoid complications (American Diabetes Association, 2023).
Type 2 Diabetes:
(Type 2 diabetes) is the most common form and is primarily linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body either becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. Early detection and intervention are critical, as lifestyle changes like diet and exercise can prevent complications and help maintain stable (blood glucose levels). In some cases, medication or insulin therapy may also be required. Regular screenings and a proactive approach to managing weight and activity levels are crucial to preventing complications like (cardiovascular disease) (Healthline, 2023).

Gestational Diabetes:
This type develops during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. It typically arises in the second or third trimester and affects about 6-9% of pregnancies. Proper management during pregnancy, including regular (blood sugar monitoring), a balanced diet, and appropriate exercise, is essential to reduce risks such as high birthweight and preeclampsia. Although gestational diabetes often resolves after childbirth, it increases the mother’s risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life. Monitoring blood sugar levels postpartum and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are vital preventive measures (American College of Obstetricians andGynecologists, 2023).
Diabetes: Insulin’s Role and Effective Management Insights
Insulin therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for those with (Type 1 diabetes) and is often necessary for individuals with (Type 2 diabetes) or gestational diabetes. Insulin assists the body in processing glucose, helping maintain healthy (blood sugar levels) within a normal range. The timing and dosage of insulin injections are critical to achieving effective blood sugar control and avoiding complications such as hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis (National KidneyFoundation, 2023).
In addition to insulin, other aspects of a comprehensive treatment plan include monitoring diet and physical activity. Combining insulin therapy with a balanced diet and consistent exercise helps individuals manage their condition and minimize complications. Collaborating closely with healthcare providers ensures insulin therapy is adjusted as needed for optimal health outcomes.
Risk Factors: Understanding the Development of Diabetes
Several key risk factors contribute to the development of the disease, including obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet, particularly for (Type 2 diabetes). Genetics also play a significant role, especially for individuals with a (family history) of the condition. These risk factors can increase susceptibility across various age groups and demographics, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing them (Healthline, 2023).
Adopting a (healthy diet) and engaging in regular (physical activity) can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. By addressing these risk factors early and proactively, individuals can prevent the onset and enhance overall health, minimizing the risk of long-term complications.
Diabetes: The Impact on Circulation and the Nervous System
This health issue can profoundly impact the circulatory and nervous systems, particularly when blood sugar levels are not well-controlled. Elevated blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, leading to reduced circulation in the limbs and conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD). This can increase the risk of infections and, in severe cases, may necessitate amputations (American Diabetes Association, 2023).
It also affects the nervous system, with complications like diabetic neuropathy causing tingling, numbness, or pain in the extremities. Such nerve damage from high blood sugar can impair sensation and coordination, making daily activities more difficult. Proper blood sugar management, combined with a comprehensive care plan, can help minimize these risks and maintain a higher quality of life.
Diet, Exercise, and Key Practices in The Management of Diabetes
“Fuel your body with balanced nutrition and exercise for optimal health.”
A balanced, healthy diet and regular physical activity are two of the most effective strategies for managing this condition. A diet that focuses on whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce spikes. Avoiding processed foods and excessive sugar intake is also crucial for effective management (AmericanHeart Association, 2023).
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and promotes cardiovascular health. Whether it’s walking, cycling, or strength training, incorporating consistent physical activity into your routine can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control and overall well-being. Together, diet and exercise form the foundation for managing the condition and promoting long-term health benefits (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023).
Lab Screening and Alternate Medical Remedies for Diabetics
HbA1c testing is a vital tool in managing and monitoring (blood glucose levels). Regular screenings, such as the A1C test, are critical for early diagnosis and effective management. The A1C test provides an overview of your average blood sugar levels over the past three months, offering insight into how well the condition is being controlled (American Diabetes Association, 2023). Early detection through these screenings is vital to prevent complications and initiate timely interventions.
In addition to traditional treatments, some individuals explore natural remedies like herbal supplements, such as cinnamon and fenugreek, which may help lower blood sugar levels. Some people also explore Garcinia Cambogia Plus, a weight loss supplement that has potential effects on weight management, particularly in those affected.
Looking for more health tips and recommendations? Look out our Health, Fitness & Wellness Essentials Post
FAQ
- What is diabetes?
Diabetes is when the body cannot properly process glucose, leading to high blood sugar due to insufficient insulin or the body’s inability to use it effectively (American Diabetes Association, 2023). - How is diabetes managed?
Management includes medication, blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, and regular exercise. Consulting a healthcare provider for a personalized plan is crucial (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023). - What role does insulin play?
Insulin helps glucose enter cells for energy. In diabetes, insulin therapy is often needed to maintain normal blood sugar levels (National Kidney Foundation, 2023). - Are there natural remedies?
Some supplements like cinnamon and fenugreek may help, but they should complement traditional treatments and be used under medical supervision (National Institutes of Health, 2023). - How often should I screen for diabetes?
Screening is recommended every three years from age 45 or earlier if you have risk factors like obesity or family history (American Diabetes Association, 2023). - What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and testing (Healthline, 2023). - Can gestational diabetes be managed effectively?
Yes, through a balanced diet, regular blood sugar monitoring, and physical activity during pregnancy. Consulting a healthcare provider for a tailored plan is crucial (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2023). - What are the long-term complications of unmanaged diabetes?
Unmanaged diabetes can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, vision loss, and nerve damage. Proper management can significantly reduce these risks (American Diabetes Association, 2023). - Can Type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly lower the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023). - Is weight management important for diabetes care?
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing diabetes and reducing complications. Supplements like Garcinia Cambogia Plus may aid in weight management but should be used under medical advice (Healthline, 2023).
Key Takeaway
- Early diagnosis and diabetes management are essential to prevent complications.
- A healthy diet and regular exercise are key to managing diabetes and improving health.
- Insulin therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining blood sugar levels.
- Regular screenings, such as the A1C test, are vital for effective diabetes management.
- Natural remedies may provide additional support but should be used under medical guidance.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a manageable condition with the right approach. By understanding its causes, focusing on prevention, and managing it through diet, exercise, and insulin therapy, you can improve your health. Stay proactive about screenings, consult your healthcare provider regularly, and explore conventional and natural remedies to support your journey. Through ongoing care, awareness, and lifestyle adjustments, you can achieve effective diabetes management and health improvement.
References
-
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Recurrent Infections and Immunodeficiencies. 2024, www.aaaai.org.
- American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Symptoms. 2024, www.diabetes.org.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gestational Diabetes. 2024, www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/gestational.html.
- National Institutes of Health. Diabetes Overview. 2024, medlineplus.gov/diabetes.html.
- American Heart Association. About Diabetes. 2024, www.heart.org/en/health-topics/diabetes/about-diabetes.
- National Kidney Foundation. Diabetes and Kidney Disease. 2024, www.kidney.org/atoz/content/diabetes.
- Healthline. Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. 2024, www.healthline.com/health/difference-between-type-1-and-type-2-diabetes.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is not intended to replace professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your primary care physician, nurse practitioner, or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Before starting any new exercise regimen or taking supplements, particularly if you have medical conditions or are on any prescription drugs, it is essential to consult with your primary care provider. They can help you assess whether any changes are safe and appropriate for your health status.
Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it based on information from this website. Never discontinue or change any prescribed medications without first consulting your healthcare provider.
Inspiring Insight
Embrace The Journey, Not Just The Destination.

— Marjorie DiCarlo, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H.
🌱 More Wellness Reads 🌱
 🌱 Why Indoor Allergies Feel Worse at Night — And What You Can Do About It 🌱
🌱 Why Indoor Allergies Feel Worse at Night — And What You Can Do About It 🌱
 🌿❤️ Boost Your Mood Naturally With These Feel-Good Foods ❤️🌿
🌿❤️ Boost Your Mood Naturally With These Feel-Good Foods ❤️🌿
 🍃10 Empowering Tips for Healthy Eating to Manage Hypertension🍃
🍃10 Empowering Tips for Healthy Eating to Manage Hypertension🍃
 Is There a Correlation Between Osteomalacia and Fibromyalgia?
Is There a Correlation Between Osteomalacia and Fibromyalgia?
 🌿AllHealthFit1 Health and Wellness Blog Archive🌿
🌿AllHealthFit1 Health and Wellness Blog Archive🌿
 🌱 Stay Ahead of Silent Killers: Monitor Blood Pressure, Sugar & More 🌱
🌱 Stay Ahead of Silent Killers: Monitor Blood Pressure, Sugar & More 🌱
 🍃 5 Everyday Habits That Secretly Harm Your Eyes and How to Fix Them! 🍃
🍃 5 Everyday Habits That Secretly Harm Your Eyes and How to Fix Them! 🍃
Powered by YARPP.
